
Water pollution causes millions of fatalities worldwide each year, with more than 90 per cent of these deaths happening in low- and middle-income countries, demonstrating uneven access to essential infrastructure that exists even to date. As the globe prepares to embrace the industrial revolution 4.0, emerging technologies provide effective solutions that are both time and cost-efficient while being less prone to error, writes Muddukrishna A.S, Urban Planner, Associate, Centre for Urban Governance, Haryana Institute of Public Administration (HIPA, State ATI of the Government of Haryana).
Water pollution causes millions of fatalities worldwide each year, with more than 90 per cent of these deaths happening in low- and middle-income countries, demonstrating uneven access to essential infrastructure that exists even to date. The manual nature of the current approaches to combat water pollution makes the disparity even more pronounced, due to the time and money-consuming nature of these manual methods. As the globe prepares to embrace the industrial revolution 4.0, emerging technologies provide effective solutions that are both time and cost-efficient and less prone to error. These data-driven solutions would not only aid in bridging the gap but also offer effective & efficient tools to address the water pollution problem. Several of which are discussed below:

The general architecture of IoT-based water quality monitoring and control system
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/General-Architecture-of-IoT-based-water-quality-monitoring-and-control-system_fig8_342278197
IoT-based water quality monitoring

“Internet of Things” often known as the IoT, is a network of connected digital, mechanical, and computer objects that have been given special identification numbers (UIDs). What makes them special is their ability to transfer data over a network in real-time without requiring human- to-human or human-to-computer interaction. It enables the sensors to capture and transmit real-time water quality in terms of pH, conductivity, dissolved oxygen, temperature, biochemical oxygen demand, total dissolved solids, and conductivity etc. The IoT facilitates the administration to make effective data-driven decisions. At the same time, demonstrating the effectiveness of initiatives in real- time to the public, inducing the factor of transparency in governance.
Also Read | Living with subsurface pollution by wastewater irrigation

Geospatial analytics based on hyperspectral imagery for water quality analysis
Hyperspectral imaging is a remote sensing technique that uses reflectance in spectral bands, based on which water quality parameters like sediment, dissolved organic carbon (DOC), carbon concentration etc can be measured. The fact that this technique can cover enormous areas and multiple water bodies without being on the field makes it unique. The geospatial data can be used to identify sources of pollution and areas of concern, enhancing the monitoring and decision-making capability to address the issue of water pollution.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Big Data
With enormous volume, velocity and variety of data being generated through various sources in different forms (structured, unstructured and semi-structured data), it becomes a near impossible task to transform this data into wisdom for taking actionable decisions in real-time. Since ‘data not converted into wisdom and wisdom not being transformed into actions are simply useless’, the need for artificial intelligence emerges.
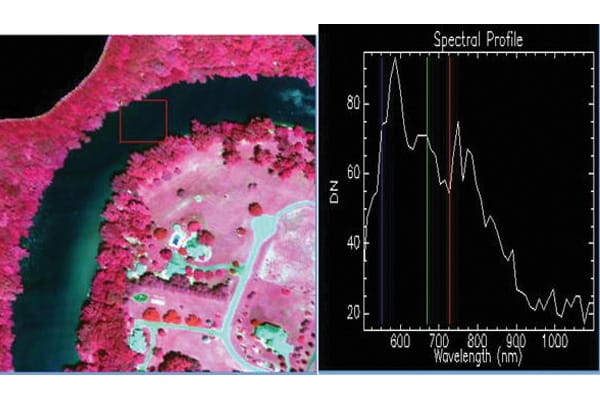
Hyperspectral Imagery
Source: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/69219
AI emerges from the thought process that human thought can be mechanised, and is defined as the ability of machines to learn, act, sense, and comprehend rationally. It is due to this very nature that it can be used to:
Monitor and inspect water quality through pattern recognition and machine learning
AI can be used to detect biological and chemical contaminants in the water. Clean water AI is an example of a deep neural network model that uses IoT-based high-definition microscopic cameras which can track harmful microbes and effluents in real-time. The application denotes the hazardous locations on the map. Simple test devices like this would significantly aid in disease prevention and save thousands of lives across the globe, where access to clean water is a persistent problem.
Detect untreated sewage spills
Untreated sewage spills can be detected in near to real-time. AI systems compare real-world circumstances to expected water levels based on past data using data from the IoT-based devices, remote sensing data, discovering discrepancies and notifying operators in advance using predictive modelling techniques.

DIKW model
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-data-information-knowledge-wisdom-DIKW-hierarchy-as-a-pyramid-to-manage-knowledge_fig6_332400827
Identify contamination and leaks in the pipeline
An integrated AI based on sensing, communication, analytics and reporting would be an ideal way forward, as it would not only help in tackling the issue of contamination in pipelines, but would also help address the issue of Unaccounted- for-water (UFW) based on advanced Hydraulic models. These Hydraulic models can be used to develop:
● Forecasting tools: This can be used to develop a “what if” scenario for the design and operation of the water distribution network.
● Explanation and prediction tools for what occurred and prediction for what would happen in the water distribution network/ sewer network, based on which problems like network blockages could be identified before they happen. This would enable a quick investigation of the predicted blockage and prevent it from developing into an issue.
● Prescriptive tools for decision support platforms can advise on the best solutions to specific problems.
Industrial effluents
With India set to leap forward to the future as a manufacturing powerhouse with a staggering growth rate¹, it becomes essential to channel this growth into development through the funnel of social, environmental and economical sustainability. Despite strict regulations, untreated industrial effluents still remain to be one of the prominent factors of water pollution². In this context, effective monitoring of industrial effluent becomes a need of the hour, as also pointed out by NGT in its directions given to CPCB³.
Also Read | Managing urban drains for citywide wastewater management
AI-based IoT solutions offer a ray of hope to the problem of scale, where IoT-based sensors can be imbibed industries, based on which effluents can be monitored through AI in real-time. Wherein using predictive analysis, problems can be identified and addressed prior.
Way forward
With India aspiring to lead the Industrial revolution 4.0⁴ driven by AI, machine learning, 5G technology, Internet of things, robotics, biotechnology, quantum computing, etc., reorienting its strategies in manufacturing, supply chain, logistics etc.
Due to this, it becomes essential for the developmental sector also to realign its approach to tackling the fundamental issues, where emerging technologies can be used as an effective tool to achieve Sustainable Development Goals.
The article explores the scope of emerging technology through the lens of challenges that exist in the water sector. Like any other developmental sector problem, it was observed that the solutions never work in an isolated view. Implementation can be effective only when they are approached comprehensively.
Sources:
● https://www.indiawaterportal.org/ articles/ngt-seeks-monitoring- mechanism-industrial-waste- discharge
● https://www.azocleantech.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=1201
● https://www.adb.org/sites/default/ files/publication/614891/artificial- intelligence-smart-water- management-systems.pdf
● https://cimconautomation. com/2020/10/10/iccc-water- management-systemsmart-city/
1. https://www.cnbctv18.com/economy/iip-data-indias-industrial-output-rises-196-in-may-says-government-14108642.htm
2. https://indianinfrastructure.com/2021/12/31/73992/
3. https://www.indiawaterportal.org/articles/ngt-seeks-monitoring-mechanism-industrial-waste-discharge
4. https://www.business-standard.com/article/current-affairs/india-guiding-world-s-fourth-industrial-revolution-says-pm-modi-122070401285_1.html
Be a part of Elets Collaborative Initiatives. Join Us for Upcoming Events and explore business opportunities. Like us on Facebook , connect with us on LinkedIn and follow us on Twitter, Instagram.











