
Due to lockdowns imposed to prevent transmission of the Coronavirus, small businesses suffered huge losses and the transport sector has come to a halt. However, with relaxations from the Ministry of Home Affairs industries have started rev their engines again. To know about how the MSMEs and the transport sector is moving ahead towards growth and development, Arpit Gupta and Adarsh Som interacted with Nitin Gadkari, Minister for Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) and Minister for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in an exclusive interview for the eGov Magazine.
Q. How has Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan’s stimulus fund supported the roads and highways sector and MSMEs in regaining normalcy ?
Under the Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan’s stimulus fund, RBI has supported all infrastructure projects by giving moratorium against all loan payments due in COVID period. Besides RBI’s support, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has extended the following support:

- All road agencies will now be providing up to six months extension to contractors without any costs which will be covering construction work as well as goods and services contracts.
- Partial release of bank guarantees to the extent of partially completed contracts.
- Compensation of toll loss for the period for which the toll collection was suspended.
- It has been observed that the toll collection has significantly decreased which has led to cash flow issues in many projects. National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has rolled out a policy for extending cash support in the form of COVID loan at a lower interest rate to help concessionaires.
- One-time dispensation for toll revision of concessions signed before 2008 to be undertaken on the basis of WPI prevailing in December rather than March. As WPI for March was very low because of prevailing conditions in the country.
As per the relief measures provided by MoRTH under Atma Nirbhar Bharat, all-out efforts were made to extend all possible help to Contractors, Concessionaires and developers of Road Sectors by way of Time Extensions (3-6 months), relaxation in Contract provisions for ensuring cash flow, direct payment to subcontractors and release of retention money to augment cash flow, waiver of penalty in case of delay in submission of Performance Security (for new Contracts), and compensation of toll loss.
Also Read: India Spearheading

Availability, as well as the cost of credit, has been one of the perennial problems of this sector. MSME Sector survives on a very thin margin. The recently announced measures (i) Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme ( ECLGS), (ii) Distressed Asset Fund – Subordinated Debt for Stressed MSMEs (iii) Fund of Funds will help this sector in its pursuit towards mobilisation of funds both as Debt as well as Equity.
Definition: This Ministry, vide notification no. S.O.2119 (E) dated June 26, 2020, has notified composite criteria of classification of MSMEs based on investment in plant & Machinery/equipment and turnover of MSMEs. The new classification has come into effect from July 1, 2020.
Any person who intends to establish a micro, small or medium enterprise may file Udyam Registration online in the Udyam Registration portal, based on self-declaration with no requirement to upload documents, papers, certificates or proof. On registration, an enterprise (referred to as “Udyam” in the Udyam Registration portal) will be assigned a permanent identification number to be known as “Udyam Registration Number”. An e-certificate, namely, “Udyam Registration Certificate” shall be issued on completion of the registration process. The total new registration is 33051 as on date.
With the change in criteria of classification of MSMEs, Enterprises with an investment of up to Rs 50 crore and turnover of up to Rs 250 crore will now be termed as medium enterprises, investment of up to Rs 10 crore and turnover of up to Rs 50 crore will be termed as small enterprises and investment up to Rs 1 crore and turnover up to Rs 5 crore as micro-enterprises.
Under Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan’s stimulus fund for government procurement, tenders up to Rs 200 crore will not be regarded as global tender. Earlier, a majority of MSMEs were unable to match the requirements due to the tender being global. With this change in classification criteria, MSMEs could now be able to participate in Government/ Highways related Tenders, which will help the MSMEs to grow their business and help MSME sector to come to normalcy faster.
Change in classification criteria will help firms increase their capacity without losing the benefits of being a small unit.
Delayed payment: On delayed payment, the matter has already been pursued with DPE and other Departments at Secretary level through D.O. Letter dated 18.05.2020. The Samadhaan data as below shows that the cases of delayed payments against central government departments /CPSEs /State Govt/Central Ministries have been mutually Settled/ disposed of in a speedy manner.
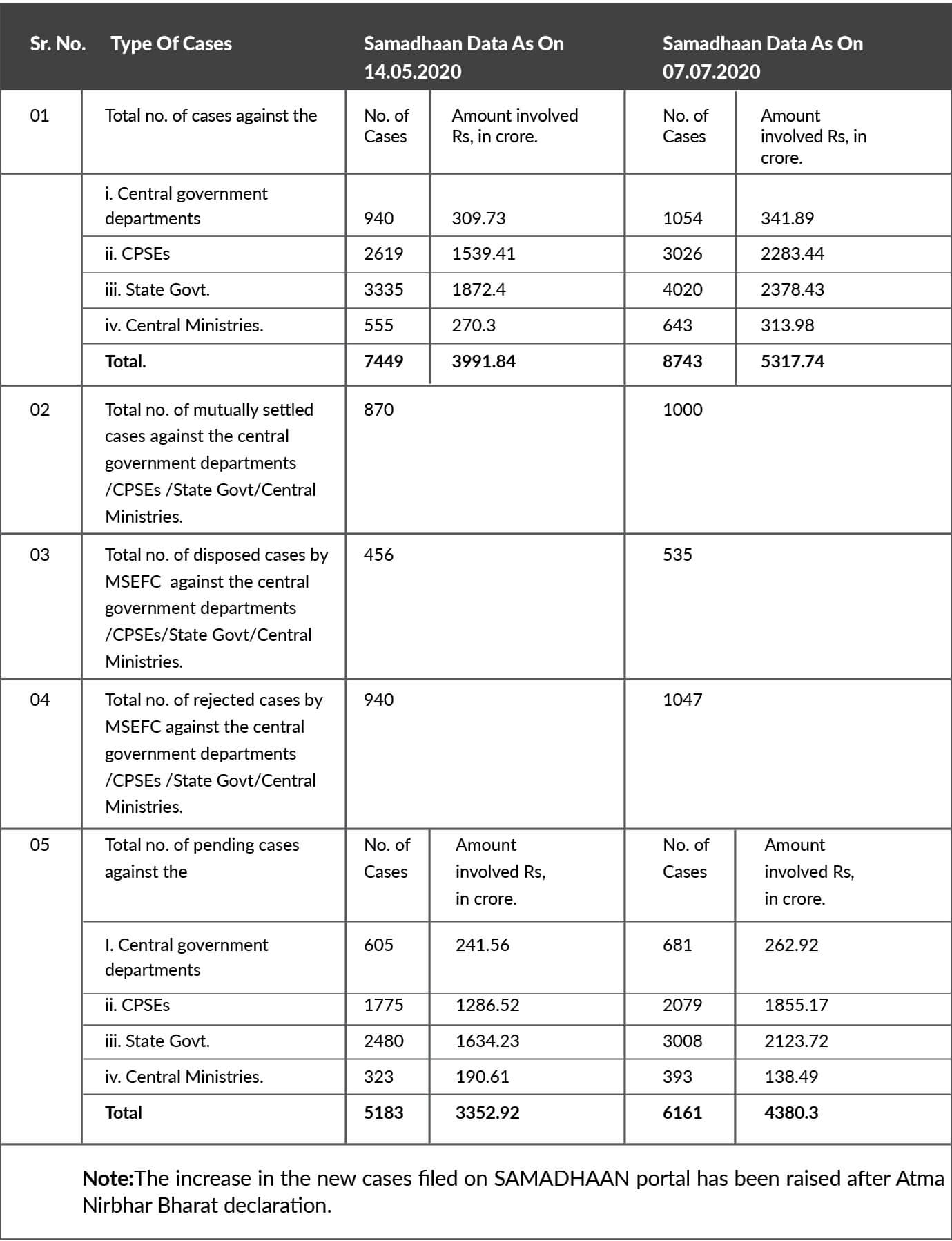
The resolving of delayed payments problems will increase the liquidity of MSMEs and increase their operational efficiency.
Procurement & Marketing Support:
Atma Nirbhar Abhiyan is a self-Reliant Indian Movement. It includes Package to cater to various sections including cottage industry, MSMEs, labourers, middle class, and industries, among others. It includes the following interventions for MSMEs related to Marketing Support. In the wake of the widespread COVID pandemic, accessibility of conventional modes of the market to the MSMEs have been greatly impacted and hence, the providing e-marketing platforms are the plausible solution.
- As regards, Procurement & Marketing Support to MSME is concerned, efforts are being made to create e-market linkage for MSMEs that could act as a Stopgap arrangement to the Conventional trade fairs and Exhibitions. Various trade bodies and Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) are being consulted to onboard them for holding Virtual trade fairs and Exhibitions so that trade for MSMEs could be facilitated.
- The process of establishing a connection with e-commerce companies has been initiated to discuss ways and means to provide concessional membership to the MSMEs. Meeting with e-Commerce companies to deliberate the way forward has started.
- Organising India Global Joint Venture Shows not only to facilitate trade between Indian MSMEs but also facilitating Joint Ventures in areas of technology transfer, investment in equity, investment in startup companies through venture capital and angel funding, tie-ups with OEMs, tie-ups in areas of Skill development, tie-ups on Brand usage and network of businesses across the globe, and sharing of best business practices and management knowledge and information. A Webinar for consultation with the trade bodies will be held shortly to proceed further in the matter.
Q. As it is known that there are business opportunities coming up as many companies are shifting their manufacturing from China, how do the MSMEs in India prepare to grab the opportunity?
For sustainable and robust growth of MSME Sector, M/o MSME has several schemes which would help Indian MSME to grab the opportunity. These schemes include the following:
Credit and Financial Assistance to MSMEs
- Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)
- Credit Linked Capital Subsidy Scheme for Technology Upgradation (CLCSS)
- Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE)
- 2 percent Interest Subvention Scheme
Skill Development and Training to MSMEs
- Entrepreneurship and Skill Development Programme (ESDP)
Infrastructure Support to MSMEs
- Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI)
- MSE Cluster Development Programme (MSE-CDP)
Technology Upgradation and Competitiveness Scheme for MSMEs
- Design Clinic Scheme
- Lean Manufacturing Competitiveness Scheme (LMCS)
- Digital MSME Scheme
- Financial Support to MSMEs in ZED Certification
- Scheme Support for Entrepreneurial and Managerial Development of MSMEs through Incubators
- Building Awareness on Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs)
- Tool Rooms & MSME Technology Centres
Procurement and Marketing Support to MSMEs
- Procurement and Marketing Support (PMS)
- Scheme Procurement from Micro and Small Enterprises (MSEs)
For helping MSMEs, we have Development Institute: 32, Branch-26 and 18 Technology Centres covering all States/UTs. Recently the Government has taken a series of measures to contain the adverse impact of COVID19 on the MSME Sector. These include Rs 20,000 crores Subordinate Debt for Stressed MSMEs, Rs 50,000 cr. Equity infusion for MSMEs through Fund of Funds, MSME receivables from Gov and CPSEs to be released in 45 days, Definition of MSMEs revised, etc.

Q. Is the road ministry planning to install a system which can automatically track the movement of ambulances and fire engines and can send alerts through traffic signals to people on roads to make the passage traffic-free or something similar?
The Ministry has been working on such a system. There are a few pointers to reflect the efforts from the ministry to adopt a smart approach using tracking systems to clear traffic for emergency situations.
- The Ministry has mandated the Vehicle Tracking System and specifications for such a system are already in place. It provides for vehicle tracking and emergency buttons.
- The system for Tracking for Public Service Vehicles (Commercial ones mainly) as a VTS device has been fitted in all new vehicles since 1st Jan 2019.
- For the old vehicles, we have given the powers to the State Government to specify the implementation date.
- The VTS based system has the functionality to track the ambulances, fire service vehicles.
- Further, the Government of India is financing a project for implementing the Back end Control IT system in States under Nirbhaya Project which will help in monitoring vehicles fitted with VTS.
Q. What are the major challenges that authorities face when it comes to EV infra establishment?
Major challenges in the creation of charging infrastructure are as under:-
- High Cost
- Limited Domestic Manufacturing (Charging Guns are being imported and assembled in India)
- Low Volume is resulting in a lesser number of players from participating
Q. As smart roads are a new concept, please throw some light on what smart roads actually are and their significance?
Smart Highways are highways which blend new technologies in improving and strengthening highways and making them smart.
Technology: Smart highways use technologies like Highway Traffic Management System (HTMS) that includes Variable Message Signs (VMS) CCTV, Video Incident Detection System (VIDS), Warning Devices, Over Speed Checking System, Weigh-in-Motion, Pavement Management Systems, etc. to ensure that the highway provides world-class safety and comfort to the users.
Going Green: Environment friendly, as they use solar power for lighting on the entire stretch and plantation of trees along the stretch of the road is mandatory. In the case of space constraints, there could be vertical gardens with drip irrigation facilities. 
Better ecosystem: These highways will have no red lights, no parking problems, sound and air pollution free environments along with our other features. These highways will provide speed and have local markets, restaurants, shopping complexes where the local residents get employment.
Smart tolling: Electronic Toll Collection (ETC) is part of the broad initiative in smart highways which is aimed at avoiding congestion at toll plazas and making payment of toll easy and quick. Further, Eastern Peripheral Expressway uses a closed tolling system in which the collections are made only on the distance travelled and not on the entire length.
Prototype: Eastern Peripheral Expressway (EPE) country’s first smart highway has been operational since May 2018. The highway is equipped with smart and intelligent highway traffic management system (HTMS) and video incident detection system (VIDS) and is set a benchmark in highway construction by being environment-friendly with world-class safety features and smart/interactive infrastructure. The street lights are powered by 8 solar power plants having a capacity of 4000-kilowatt (4 MW). 2.5 lakh trees have been planted along the highway.
Q. In dense cities like Delhi, there are a lot of parking issues that people face every day. Can multi-level car parks and underground parking for every residential colony be a potent solution for the woe?
In dense cities like Delhi, Multi-level Parking System is an efficient system and shall provide relief to the present woeful parking scenario, since they come with a number of advantages; the most vital advantage is the provision of a good number of parking slots within minimal space. The key advantages of Automated Multilevel Car Parking are as under:
Optimal utilization of space, lower maintenance and operational cost.∙ Safeguard against on-road damages and theft.∙ Environment-friendly nature (leads to more green spaces for plantation,∙ etc). Comfortable for the drivers, saving time and fuel (since one does not∙ have to drive around for locating parking space). Minimum Manual Intervention.∙ Can be above ground or underground or combination of both.∙ The concept of Automated Multilevel Car Parking System shall substantially∙ contribute to the Smart City development programme as well.
Q. Recently, on World Bicycle Day, many environmentalists and even the government leaders advocated cycling. Sir, are the streets of Delhi or Mumbai or any other metro city properly equipped with cycling infra and safe for cyclists?
The Government is taking steps to ensure that safety features are built-in at the stage of design, manufacture, usage, operation and maintenance of both motorized and non-motorized vehicles in line with international standards and practices in order to minimize adverse safety and environmental effects of vehicle operation on road users (including pedestrians and bicyclists) and infrastructure.
Q. In India, how are we working on hydrogen-based fuel? What steps are being taken to shift the major chunk of fuel consumption on biodiesel or other biofuels?
This Ministry is in the process of notifying standards for the safety evaluation of Compressed Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle and creating a road map for the development and further adoption of the Technology of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle.
Further, Ministry of Road Transport & Highways has notified following mass emission standards-
- E-10 is notified vide GSR 412(E) dated 19.05.2015 for blending 10 percent Ethanol blending with gasoline. The materials of gasoline vehicles are currently compatible with E-10 fuel.
- E-85 has been notified vide G.S.R. 682(E) dated 12.07.2016 for 4 Wheeled vehicles, 2W, 3W.
- E-85 enables newly manufactured gasoline vehicles to mix gasoline and ethanol (85 percent by volume). Under the same notification, E-100 and ED-95 [95 percent ethanol and 5 percent additives (co-solvent and corrosion inhibitors and ignition improvers)] have been notified.
- Mass emission standards for M-15 or M-100 and MD 95 have been notified vide G.S.R. 490(E) dated 24.05.2018 for M and N category vehicles and also 2W and 3W. M-15 implies that newly manufactured gasoline vehicles mix gasoline and methanol (15 percent by volume). MD-95 [95 percent methanol and 5 percent additives (co-solvent and corrosion inhibitors and ignition improvers)] fuel.
- The Ministry has notified the mass emission standards for new vehicles fitted with compression ignition engines compatible to run on a mixture of bio-diesel up to 100 percent, vide GSR 412(E) dated 11.04.2016.
- The emission standards for Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) notified vide G.S.R 889(E) dated 16.09.2016 refers to vehicles fuelled with a blend of biodiesel (7 percent) and diesel.
- Mass emission standards for Bio CNG (G.S.R. 498 (E), dated 16/06/2015)
- Mass Emission Standards for LNG. (G.S.R. 643 (E), dated 27/06/2017)
- Mass emission standards for M85 and Di-Methyl Ether (DME or D100) Vehicles
Production of Biofuel from coir pith
The demand for fossil fuels, a nonrenewable resource, is increasing day by day. Energy security of the world is vulnerable unless alternative fuels such as biofuels are developed to supplement fossil fuels. Biofuels are environmentally friendly so that fewer efforts are only needed to control the pollution caused by these. The Government of India has initiated a National Policy on Biofuels which aims at blending 20 percent of biofuels such as bioethanol and biodiesel with fossil fuels.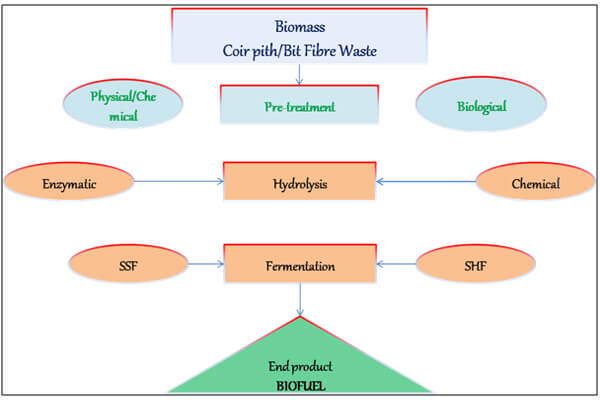
Biodiesel is a form of diesel fuel derived from plants or animals and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made by chemically reacting lipids such as animal fat (tallow), soybean oil, or some other vegetable oil with alcohol, producing a methyl, ethyl or propyl ester. Fast Pyrolysis is an effective method for the production of bio-oil under varying temperatures in the absence of oxygen. This Bio-oil could be treated as in the same way as that of conventional fuels but is less polluting.
Processes need to be developed for effective removal of lignin with minimum loss of cellulose for the effective production of bio-ethanol. The production of bioethanol involves three major steps such as Pre-treatment for the removal of lignin, Hydrolysis for the depolymerisation of cellulose and Fermentation which converts the available sugars into ethanol. These various steps need to be compared and optimised so that the method becomes effective for the production of Biofuel.
Coir pith is a by-product from the coir industry, which is a lignocellulosic material with high lignin percentage (38.5 percent) and cellulose content of 26.4 percent. Methods such as pyrolysis and fermentation are widely used for the production of biofuels from lignocellulosic materials. Coir pith which could be one of the best substrates for biofuel production needs to be utilized in an effective way so that optimised processes or conditions would give a higher yield from a minimum substrate.
CCRI has already initiated work on the extraction of biofuels from Coir Pith. A method of fast pyrolysis process has been utilised, where coir pith is subjected to a temperature of 350 to 400oC and the vapours generated are condensed to obtain the Bio-Oil. This crude bio-oil needs to be upgraded by the process of deoxygenation to obtain a better quality Biofuel. The sample of Biofuel extracted from coir pith has been tested for burning property and showed high calorific value. The work is being continued and further characterisation needs to be performed for confirmation of results.
Be a part of Elets Collaborative Initiatives. Join Us for Upcoming Events and explore business opportunities. Like us on Facebook , connect with us on LinkedIn and follow us on Twitter, Instagram.











