
 2016 has proved to be an excellent year for the Digital India programme with many key projects getting launched and many digital projects seeing unprecedented growth by the end of the year. Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, Digital India campaign pushed the use of technology to connect and empower people in every aspect of their lives, observes Priyanka Sharma of Elets News Network (ENN).
2016 has proved to be an excellent year for the Digital India programme with many key projects getting launched and many digital projects seeing unprecedented growth by the end of the year. Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, Digital India campaign pushed the use of technology to connect and empower people in every aspect of their lives, observes Priyanka Sharma of Elets News Network (ENN).
The Digital India programme was launched in July 2015 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi. Since its launch, many key IT and e governance initiatives have seen a surge in their growth, which has taken the vision of a digitally empowered India to the next level.
Last year, many milestones were achieved by the Government of India. Various schemes, products and services have been rolled out under the programme to promote e-governance efforts in the country through digitisation.
“Digital India and Smart City are the two most important initiatives of the government. Footprints  of these initiatives can be felt across the nation. The major achievement in this regard can be seen as the acceptance of these initiatives by the citizens and the states. People have started understanding the need of better infrastructure and the importance of technology,” said Pradeep Misra, Chief Managing Director of Rudraabhishek Enterprises Private Limited (REPL).
of these initiatives can be felt across the nation. The major achievement in this regard can be seen as the acceptance of these initiatives by the citizens and the states. People have started understanding the need of better infrastructure and the importance of technology,” said Pradeep Misra, Chief Managing Director of Rudraabhishek Enterprises Private Limited (REPL).
Here we look at the key achievements of Digital India programmes which took place in 2016:
BharatNet
BharatNet which focuses on bringing high-speed broadband connectivity to rural areas and plans to cover all 2,50,000 Gram Panchayats this year. BharatNet will provide e-Services like certificates, tele-health, e-Education, agricultural information etc. To provide high speed connectivity, 1,12,871 kms of optical fibre cable has been laid by the end of the last year, according to a data released by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
“We have been able to take many initiatives forward, particularly revamping the BharatNet programme. We also completed very difficult project in Left Wing Effected (LWE) states with setting up of more than 3,000 mobile towers in a very short span of time. We got the approval of the government for taking the undersea fibre cable in Andaman and Nicobar Islands which is very futuristic in its approach,” said Shashi Ranjan Kumar, Joint Secretary, Department of Telecommunications, Government of India.

 JAM
JAM
By enabling mobile number portability, the government has tried to enable a system whereby individuals can be identified with the help of their phone numbers. Through the Jan-Dhan Yojana, Aadhaar and Mobile Connectivity (JAM) trinity, the government has managed to directly transfer virtually endless benefits to the citizens and helped in removing anomalies and leakage.
“Government, municipalities and state agencies got digitised in 2016. Even the Chief Justice of India has asked the judiciary to go digital. The Government of India encouraged financial and banking sector to go digital in a big way,” said Asoke K Laha, President and CEO of Interra Information Technologies Inc.
Common Services Centres
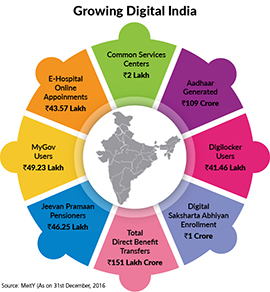
As per the data of MeitY, citizen engagement platforms such as MyGov has 19.3 lakh registered users who provide inputs, suggestions and feedback for improving governance. By the end of 2016 more than 1.66 lakh Common Services Centres have been set up by the government where government and private e-services have been provided to the citizens. These centres are the key source of providing skill development, digital literacy and financial services to rural India.

DigiLocker
The service was launched as an important facility to store crucial documents like voter ID Card, PAN card, below poverty line card, driving license, education certificates, etc. in the cloud, which is an effective and secure way to store crucial data. DigiLocker portal is also being used to engage citizens in governance through a “Discuss”, “Do” and “Disseminate” approach.
Swachh Bharat Mission mobile app
The app enables organisations and citizens to access information regarding the cleanliness drive and achieve the goals of the Swachh Bharat Mission.
Top e banking initiatives of 2016
Mobile Wallets
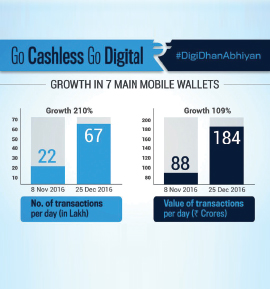
Mobile wallets emerged as the key success story of 2016. M-wallets saw a surge in their use during the last two months of 2016, owing to demonetisation. Number of transactions saw a growth of 210 per cent between November 8 till December 25, 2016, as reported by Software Technology Parks of India (STPI).
According to The Economic Times, m-wallet business will grow to 275 lakhs by 2022. This shows how India is moving ahead to become a digital economy.
“Our effort is to see that people are given various options to do digital payments. Let all the forms of the payment flourish with greater participation of the stakeholders. We believe in improvement the infrastructure side of digital payments, create awareness and capacity building and create options for people,” said Dr. Ajay Kumar, Additional Secretary, Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, Government of India.
 BHIM APP
BHIM APP
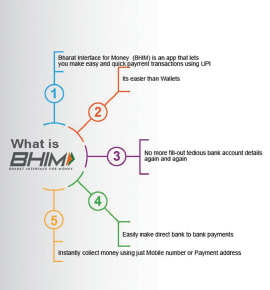
The Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM) was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on December 30, 2016. It is an app that enables fast, secure and reliable cashless payments through mobile phones. It has been developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) and is Aadhaar enabled.
As per livemint.com, BHIM app has been downloaded 5 million times and enabled 7 lakh transactions from the day it was launched till the first week of January in 2017.
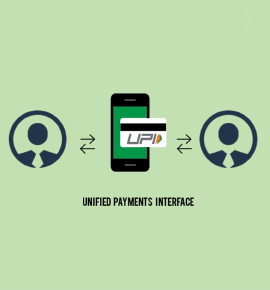
United Payment Interface (UPI)
UPI was launched with much fanfare by the Government of India in the month of August last year. It is a payment system that allows money transfer between any two bank accounts by using a smartphone. The government is planning to revamp the UPI to add more user friendly features to it.
Top e education initiatives of 2016
 Aadhaar card mandatory in entrance exam
Aadhaar card mandatory in entrance exam
For Joint Entrance Examinations, it is now mandatory for every aspirant to present their Aadhaar Card for appearing in the exam. However, students in Jammu and Kashmir, Assam and Meghalaya are exempted from this decision. It is expected that the Aadhaar Card will be made compulsory for more such entrance examinations like National Eligibility Entrance Test.
UPSC issues e-admit cards for examinations
Students appearing for the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) main examination were issued e-admit cards in 2016. Paper admit cards have been scrapped in 2015, paving way for electronic admit cards.
National Economic Depository (NAD)
NAD is an initiative of the Ministry of Human Resources Development (MHRD), launched by HRD Minister Prakash Javadekar on 9 September, 2016.
It is a unique, innovative and progressive step towards achieving digital enablement of the education records. NAD aspires to make the vision of digital academic certificates for every Indian a reality.
It is not only a database copy of the certificate records for academic institutes, but a complete system for issuing online certificates to well identified and registered students. It is an active online place for students, academic institutes and verification users.
 The Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (DISHA)
The Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (DISHA)
This scheme has been formulated to impart IT training to 52.5 lakh people, including Anganwadi and ASHA workers and authorised ration dealers in all the States and Union Territories across the country so that the non-IT literate citizens are trained and enable to actively and effectively participate in the developmental process and also enhance their livelihood.
Altogether 52.5 lakh people, including Anganwadi and ASHA workers and authorised ration dealers will be trained under the programme in two phases. In the first phase, 10 lakh beneficiaries will be trained under the scheme. Nine lakh beneficiaries will be eligible for training fee support from the government. The rest 100,000 beneficiaries will be trained by the industry and civil society partners.
“It is essential for the government to lay emphasis on spreading awareness across the populace pertaining to the content put up on websites and mobile applications for ensuring digitisation.
Users should know the importance of the information laid down online for them by the government. This will enhance their participation on government initiatives,” observes Abhishek Rungta, Founder and CEO of Indus Net Technologies.
|
 CBSE directs schools to go cashless
CBSE directs schools to go cashless
Echoing the spirit of the digital economy, the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) directed all its affiliated schools to adopt a no-cash mode of fee collection in 2016.
These initiatives have brought the entire spectrum of the educational system to the centre of the debates, highlighting the significance the education sector holds for the digital economy and demonetisation.
Top e health initiatives of 2016
 Online registration and health records in government hospitals:
Online registration and health records in government hospitals:
Online Registration System (ORS) for patients has been implemented in 56 state and central government hospitals by the end of 2016. The ORS platform allows hospitals and institutes to provide online registration and online appointment services to patients, while letting patients view medical reports online. According to the government data, there are well over 35,000 hospitals in the country, all of which will eventually be expected to have online records.
Additionally, government hospitals and Community Health Centers (CHCs) are introducing the Hospital Management Information System (HMIS) for the creation of Electronic Health Records (EHR), in a phased manner. The EHR must include disease classification, medicine and clinical terminology, laboratory data exchange, digital imaging and communication, unique identifiers for patients preferably by linking to Aadhaar etc., for interoperability.
Be a part of Elets Collaborative Initiatives. Join Us for Upcoming Events and explore business opportunities. Like us on Facebook , connect with us on LinkedIn and follow us on Twitter, Instagram.











