
 “Attacks on the enterprise are getting increasingly sophisticated. Current solutions available do not seem to be adequate given the nnovativeness, precision and persistence of these attacks,” says Sanjay Sahay, IGP, Eastern Range, Davanagere, Karnataka
“Attacks on the enterprise are getting increasingly sophisticated. Current solutions available do not seem to be adequate given the nnovativeness, precision and persistence of these attacks,” says Sanjay Sahay, IGP, Eastern Range, Davanagere, Karnataka
Research shows that 55 percent of the breaches require months or even years to contain (Veri- zon 2010 Data Breach Report). Sixteen percent of breaches are discovered via active and deliberate action. Only 24 percent of APT malware is detected by an anti-virus solution (Mandiant 2010). Logs are at the heart of monitoring and use of logs for the right purpose and in the right directions can be immensely useful. Mining of logs throws up data, which the professional can make a meaning of.
A safeguarded enterprise
Safeguarded Enterprise is the sum total of a clear-cut perception, appropriate/integrated planning, documentation, meticulous execution and dynamic/robust maintenance of enterprise security policy at awareness, attitudinal, physical, systems, processes, application and data dimensions throughout the enterprise creating a near fail-safe enterprise. Silos have ruled the world till we realised what a silo is and the way it feeds like a termite on a system, which is an integrated system, for namesake. So was the case of security in the Enterprise Business Architecture. Business, Information and Technology (BIT) were the three components.

The new approach emanates from a Gartner White Paper published in the year 2006 titled ‘Incorporating Security into the Enterprise Architecture Process’. This led to the creation of Enterprise Information Security Architecture with four critical components of Business, Information, Technology and Security (BITS). BIT changed to BITS and security became a design component itself. In the midst of the clamour for a fail-safe data regime, which would be nonetheless be a mirage, the importance of physical security should not be diluted. My visit to Indian IT companies in Bangalore has helped me confirm my belief that physical security stands at par with data security though the two are distinctly different thought processes, are different in execution and would remain to be complimentary for all times to come.
The goals of Enterprise Information Security Architecture is to provide a structure that is coherent and cohesive. As the business motive is predominant in a business enterprise, the business to security alignment in critical. Any disconnect would be critical to profitability and at times to the existence of the enterprise itself. The details ought to neatly spelt out, top down which should be synchronous in itself and synergise with the business strategy. At the end of the day, this approach helps establish a common language for information, for its free flow, clarity of communication and timely and effective response mechanism for information security within the integrated enterprise.

Key Success Factors
Awareness of the impending danger is the initiation of diagnosis. Objective diagnosis can only lead objective treatment and maintenance of a healthy enterprise both from the point of view of physical and data security. Security awareness in all its dimensions creates an environment where all success factors fall in place like a jigsaw puzzle, the people, the processes and technology. One the security awareness human plat- form are the two main technical components of Network Security and Application Security. Operating System Security, Patch and AV Management and SIEM are the three components of the final layer which can be termed as the operating, functional and the analytical layer.
Security Architecture
The key success factor is the synergy of people, processes and technology creating a seam- less security architecture, which is optimally functional and has the capability to propel the enterprise to the next level. The people part comprises of user awareness, guidance, administration and effective monitoring of the system. The processes part comprises of policies, standards, guidelines and audit capabilities. Last and the most important component in a technology driven world is technology itself manifested by the use of IPS, Firewall, AV, DLP and SIEM.
The common risks which the enterprise faces today
- Email attachments
- VPN Tunnel vulnerabilities
- Blended attacks
- Diversionary tactics
- Download from websites
- Supply chain and partners added to the network
- Microsoft’s SOAP
- Renaming documents
- Peer to peer applications
- Music and video browsers
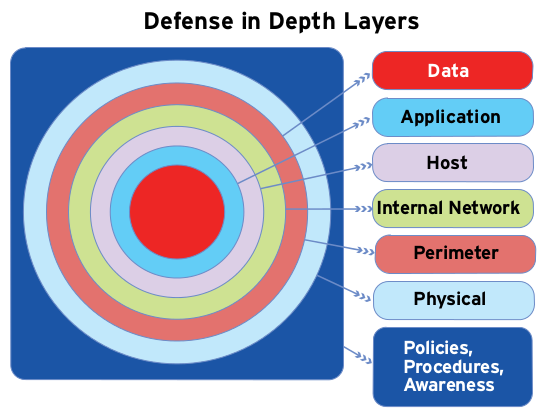
Defense of Depth
“Defense of Depth” is a concept used to describe layers of defense strategies. The components at each layer work in tandem to provide one cohesive security mechanism. This layered approach also helps localize the impact, if one element of the mechanism is compromised. The defense of depth layers concentric circles begin moving outwards with the data at the bull or the inner- most circle. The circles from the innermost to the final outside circle are data, application, host, internal network, perimeter, physical and policies, procedures and awareness.
 At the Core
At the Core
Data centre, connectivity and the application are at the core of the enterprise security. The main purpose of a data centre is running the applications that handle the core business and the operational data of the organisation. Secure application usage is the key to the creation of a secure enterprise. Secure connectivity is the backbone. The Karnaktaka State Police broadband networking is a intranet named KSPWAN which is a combination of 39, 2 Mbps MPLS leased lines for big offices, 512 Kbps 1400 VPNoBB connections covering all police stations and small offices and 8Mbps internet leased line with and aggregation bandwidth of 32 Mbps working as a single network of 5,000 computers across the state working out of a single server located at the KSP Data Centre. The choice of intranet over internet is the first decision towards security of the enterprise, which is slowly becoming the norm in enterprises across the globe. Application/s is at the heart of the enterprise. An ERP created for the enterprise aligns to all its tasks and activities also takes care of all the staff functions, which run co-terminus with the business functions. Secure ERP on an intranet is what we are all heading for.
The Application Data Security Lifecycle (ADSL)
The diagram clearly elucidates the role of different components of the ADSL. The life- cycle as is the case with concept and process starts with the assessment encapsulating the configuration/usage of servers and data, test configuration, evaluate the inherent risks and also assess how and by whom the data and applications are used. Setting polices and controls are the subsequent tasks. The policies should be automatically created considering the right mix of business and security considerations with the flexibility to adapt to user changes and support granular policies and controls. Monitoring and enforcing is more important than creating the policies itself. The separation of duties should be ensured simultaneously with user account- ability. The transaction details should be in a comprehensive manner and alerts and blocks should be resorted to in real time.
Security Information & Event Management (SIEM)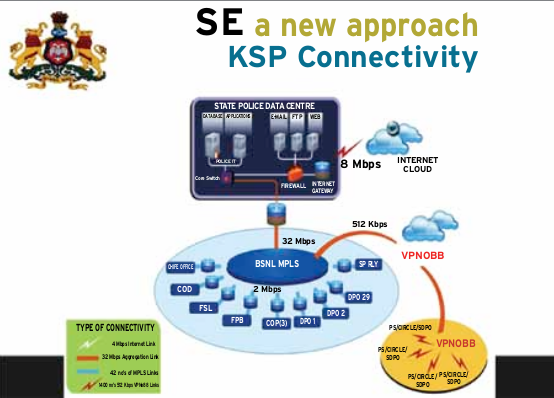
SIEM, an intelligence platform helps safeguard the business by giving complete visibility into the activities across the IT infrastructure. It fulfils the functionalities, which will be not be emanated out of single activity logs and with- out this software system no correlation can be mapped or understood, leave aside taking any correctional action. Logs are the cornerstone of all activities and making meaning of the logs as per our requirements is of great importance. The functionalities being attended to by this software are asset discovery, threat detection, vulnerability assessment, event collection, correlation, event management and log storage. The SIEM capabilities comprise of data aggregation, correlation, alerting, dashboards, compliance and retention.
Cloud – The Final Frontier
Cloud computing has turned out to be the final frontier, but enterprises my still take sometime to switch over to complete cloud environment. There are large number of security issues/concerns associated with cloud computing, which can grouped into two, firstly security issues faced by cloud providers and secondly security issues faced by their customers. The provider must ensure that their infrastructure is secure and client’s data and applications are protected. The customer must ensure that the provider has taken proper security measures to protect their information.
Single Sign On
Single Sign On, SSO, is a property of access control of multiple related, but independent software systems. Conversely, Single Sign Off, is the property whereby the single action of signing out terminates access to multiple software systems. The benefits we derive out of this system are as follows:
• More secure
• Reduces password fatigue
• Reduces time spent for re- entering passwords
• Reduces IT costs – helpdesk calls pertaining to passwords etc
• Security on all levels of entry/exit/access to systems
• Centralised reporting for compliance adherence
Cloud – Virtualisation
The extensive use of virtualisation in implementing cloud infrastructure brings unique security concerns for customers of a public cloud service. Virtualisation alters the relationship between the OS and the underlying hardware – be it computing, storage or even networking. The use of this technology introduces an additional layer – virtualisation – that itself must be properly configured, managed and secured. Specific concerns include the potential to compromise the virtualisation software. While the concerns are largely theoretical, they do exist.
Challenges
What we are witnessing today are advanced cyber threats, and collaboration is the key in dealing with them. No single organisation can respond positively given the nature of the challenge posed on enterprises today. There is need for the creation of an Advanced Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) for protecting the country’s enterprises from the rapidly evolving advanced and persistent cyber threats. ACSC would strengthen short term defences and long term capability. Actionable intelligence to bolster an organisation’s defence in the short term and generate new defensive strategies and R&D in the longer term would be the logical guiding principle. The near term results would be application of front line analytics, medium term results would be the application of New “ Predictive Analytics” development and the long term results would true Research & Development which would throw up innovative security solutions for the enterprise. Though it would be time taking yet it would be worthwhile to leverage on sustainable and continuous research improving the enterprise security by leaps and bounds. The other challenges include cloud computing with virtualisation. With mobility becoming the order of the day, this would remain an area of exclusive concern and most gadgets would be internet enabled where compromising security is easier than in a closed environment. The complexity of IT security gets con- founded with innumerable applications, the processing power, the World Wide Web inter- face, cross enterprise collaboration and the like. Cloud computing, though in its nascent stage, has thrown a major challenge to IT security. A range of innovative ideas are needed to keep the IT industry growing in a secure environment and cause maximum benefit to the people.
Be a part of Elets Collaborative Initiatives. Join Us for Upcoming Events and explore business opportunities. Like us on Facebook , connect with us on LinkedIn and follow us on Twitter, Instagram.











