
Background
Rivers play a vital role in the development and growth of cities. They provide essential resources and support economic activities, along with a wide range of other ecosystems. However, rapid urbanization and unsustainable practices have taken a toll on these precious water bodies, leading to pollution, encroachment, and ecological degradation. The major focus of Indian cities has been to prevent pollution from entering the rivers. However, there is a growing recognition that river management needs to encompass a broader spectrum of measures that encompass environmental, social, and economic aspects.
The National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA), in collaboration with The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) and other partners, has taken the lead in advancing river-sensitive development in our cities and has developed various frameworks and guidance documents to facilitate the adoption of river-sensitive development practices. Urban River Management Plans (URMPs) and River-Sensitive Master Plans and guidelines are a few knowledge avenues that will play a key role in river-centric development.


In order to create a robust avenue for interaction and exchange of ideas among the riverine towns and cities, a common platform has been imagined to form an alliance. This will help to forge new paths and special opportunities for cities to learn from one another, exchanging knowledge and experiences and serving as inspiring examples to motivate others to embrace progressive action for river-sensitive development. The River Cities Alliance (RCA) was launched on 25 November 2021. RCA’s core objective is to serve as a platform for river cities in India to ideate and discuss solutions for the sustainable management of urban rivers. What began as an alliance of 30 cities has now grown into a formidable network of more than a hundred cities, with the city of Aarhus from Denmark as an international partner city.

River Centric Urban Development
Riverine systems such as water bodies, wetlands, lakes, drains etc have been missing out in the priority areas of urban planning process in most of the cities. The planning instruments and tools need to be exercised wisely to incorporate river sensitive elements in various layers of plans. It is evident that no new tools or instrument has to be conceptualized, in fact the existing tools and instruments can be exercised sensitively to support a proper river management system.
Various avenues developed under the alliance like River City Alliance as mentioned above will provide cities with an actionable path to work on the holistic development of their rivers includes strategic policy guidance for making river sensitive plans, strategic framework for managing urban rivers which are further supported by various Knowledge resources, tools and instruments in making these avenues actionable. Some of the major avenues are discussed below.
Master Plans and River Management
NIUA and NMCG have developed the Strategic Guidelines for “River- Sensitive Master Plans,” which aim to help city planners integrate river- sensitive thinking into Master Plans across the basin and the country. The guidelines elaborate on seven avenues within Master Plans that address river-related urban challenges, including land use assignment, development control regulations, and norms and standards for floodplain activities. Creating a Master Plan Vision for the River involves setting a broad vision that clarifies the city’s connection with the river, fostering value for the river in the Plan.
The river baseline entails establishing a robust knowledge baseline of the river and its interaction with the city, informing river-specific strategies and understanding its contextual setting. Several national and state policies in India, such as Jal Shakti Abhiyaan, Draft National Water Policy, and National River Conservation Plan, impact river management. Cities can develop their own policies/strategies, considering citizen engagement,
blue-green continuum, urban forestry, and riparian plantation. Whereas the land use planning within the river influence zone must preserve the area’s natural ecology through delineation, appropriate land use assignments, and restricted activities. Development Control Regulations (DCRs) limit development in the river influence zone, considering factors like minimum plinth levels and the prohibition of basements. Norms and standards facilitate regulated growth and maintain the quality of riverine resources, encompassing buffer zones, environmental flow, and channelization.
It is evident that the Master Plans have the authority to make recommendations and provide directions to benefit the riverine systems, such as water demand management and penalties for polluters. River-related special projects, like eco-friendly ghats and green infrastructure, can be proposed with detailed action plans and directions for development agencies.
River management framework
The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) and the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA) have developed a common URMP framework for river cities across India. The framework aims to help river cities achieve a state where the river will be able to support a habitat for biodiversity to thrive and provide opportunities for economic
development.

The URMP framework is a holistic yet simple strategic framework that should be adopted by the river cities to manage the rivers within their stretch. The framework has various elements in terms of objectives that include river-sensitive behavior among citizens, riverfront development, river water quality management, river ecology and biodiversity conservation, riverfront amenities, and river governance.
Detailed directions on how the river cities should prepare their own URMPs are also determined, further simplifying the process of plan preparation. Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) is a vital element of the URMP, providing a mechanism to evaluate the progress of implementation of the URMP vis-à-vis its objectives.
In conclusion, the URMP framework provides a strategic approach to managing urban river stretches in the Indian cities. It aims to achieve a state where the river can support a habitat for biodiversity to thrive and provide opportunities for economic development.
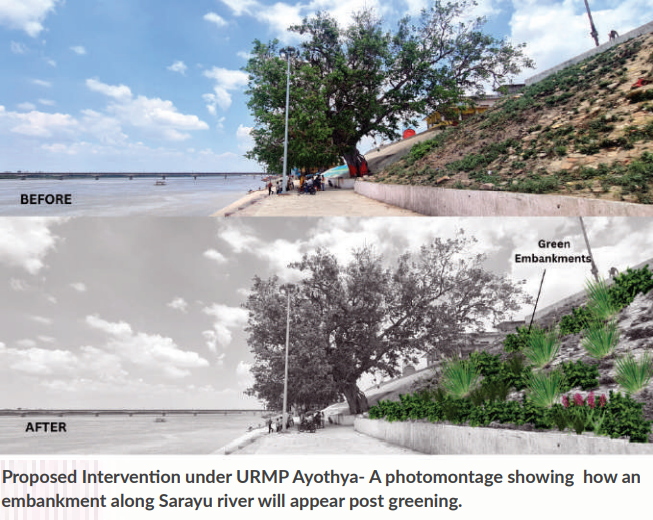
The development of URMP has not just remained a document on paper but has been prepared as a living document for various RCA cities in the Ganga basin as well as Non-Ganga basin. Kanpur, Ayodhya, and Sambhaji Nagar have their Urban River Management Plans ready, and identified interventions are being incorporated under various urban development projects. URMPs for Moradabad and Bareilly are set to be launched in August, and URMPs for 25 more cities are to be prepared in the next one year.
The River Cities Alliance (RCA) proposes eco-friendly activities for its member cities to foster a healthy river-citizen connection. To mention, initiatives include the River Festival in Aurangabad, controlled religious activities for preservation of an ancient ghat, and a Turtle Hatchery in Moradabad, as part of the Urban River Management Plan (URMP). These interventions promote community engagement, cultural preservation, biodiversity conservation, and the revitalization of water resources.
Water body Rapid Health assessment
The water bodies are the most important elements of Riverine systems. The underground hydrology connects the riverbed, water bodies, and the aquifer systems. The health of the river and the quality of underground water are heavily dependent on the health and quality of water bodies. To quickly assess the health of the water bodies, an ‘Urban Water Body Diagnostic Tool’ has been developed by NIUA, NMCG, and UNESCO. The tool is intended to serve as a decision support system for managing the water bodies within cities. This tool helps in identifying and prioritizing actions for the rejuvenation of water bodies.
This web-based diagnostic tool will enable cities to conduct a holistic rapid assessment of all their water bodies periodically to identify immediate actions for their management. The tool can be used by city administrators, municipal officers, researchers, and practitioners associated with the management of urban water bodies. The database of water bodies, comprising the locations, quality, encroachment, and other ecological factors, will help cities prioritize the water body management plans in a phased manner.
Training and capacity building of city officials
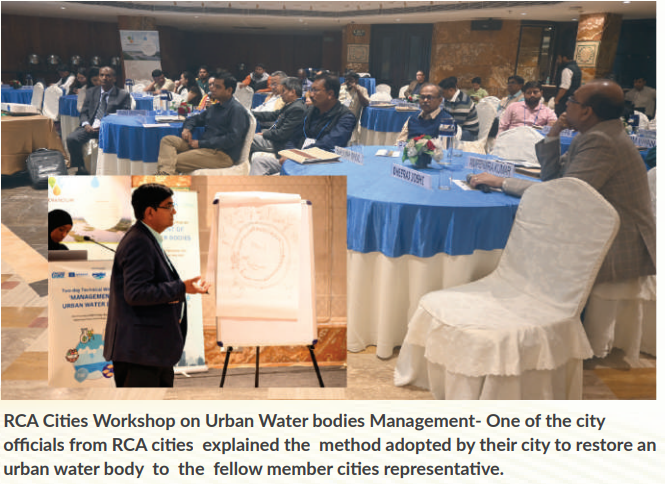
There is a big gap in terms of knowledge and understanding for the management of riverinn system in our cities. Therefore as an integral part of the River Cities Alliance (RCA), training workshops will play a pivotal role in engaging with member cities. These workshops are conducted regularly, providing a valuable platform for cities to embrace a river-sensitive development approach. Through these sessions, cities have the opportunity to openly discuss their concerns regarding river and water management, seeking solutions with the support of sector experts. What sets these workshops apart is the emphasis on peer-to-peer learning. Officials from different cities, who have successfully tackled similar challenges, come together to exchange ideas and share their innovative solutions. This collaborative approach leads to the development of practical solutions that go beyond traditional engineering approaches.
By leveraging the power of collective knowledge and experience, the training workshops organized under RCA empower cities to adapt and implement sustainable strategies for river and water management. This enables them to overcome hurdles, enhance their understanding, and pave the way for more effective and impactful outcomes.
Dhara – Annual river summit
To brainstorm, co-learn, and share experiences, an annual meeting of RCA city officers, including the municipal commissioners, is called every year. In 2022, the first RCA member cities meeting, under the title “Driving Holistic Action for Urban Rivers (DHARA),” was held in Pune, one of the RCA member cities. DHARA was a unique opportunity for RCA city representatives (Municipal Commissioners/Executive Officers and Senior officials) to spend dedicated time brainstorming, discussing, and learning about solutions for urban river management.

The focus of the event was to inspire member cities to proactively take up progressive action for urban river management in their respective cities while also addressing key emerging issues and challenges related to river management in urban areas. This, in turn, would help in preparing a work plan. DHARA also served as a platform for inter-city dialogues and communication, promoting peer-to-peer learning. DHARA 2023 featured representation from RCA members, central and state government dignitaries, think-tanks, NGOs, students, young leaders, national and international experts, funding agencies, the private sector, media, and others.
Conclusion and way forward
River is the lifeline of cities, and this fact has been widely supported through the popular tagline “”स्वस्थ-धारा, संपन्न किनारा” (Healthy stream, prosperous riverine settlements) emerging from DHARA 2022. The rivers should be saved, conserved, and considered as essential elements of urban planning. People- river connections should be improved to make citizens sensitive about rivers and water bodies. Promoting river-sensitive development is crucial for the sustainable future of cities. By adopting a holistic approach that considers the environmental, social, and economic aspects of urban rivers, cities can reclaim their water bodies as valuable assets.
Preserving the health of rivers, managing water resources sustainably, mitigating flood risks, enhancing urban aesthetics, strengthening social cohesion, and unlocking economic opportunities are all essential elements of river-sensitive development, which are encapsulated under the River Cities Alliance. Embracing this approach will not only create greener and healthier cities but also nurture vibrant communities that thrive alongside their rivers, fostering harmonious coexistence between urban life and nature.
Views expressed by Lovlesh Sharma, Member, National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA)
Anirudh Soni, Member, National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA)
Be a part of Elets Collaborative Initiatives. Join Us for Upcoming Events and explore business opportunities. Like us on Facebook , connect with us on LinkedIn and follow us on Twitter, Instagram.
"Exciting news! Elets technomedia is now on WhatsApp Channels Subscribe today by clicking the link and stay updated with the latest insights!" Click here!













