

Our key agenda is to bring about qualitative improvements in governance so as to provide better services to the common man, asserts Rajasthan Principal Secretary(IT&C) Shreemat Pandey
Information & Communication Technologies (ICT) has been identified as an important strategic tool to bring about improvements in the productivity and performance of the government and to inculcate deeper citizen involvement within the governing process, while taking steps to bridge the prevalent digital divide.

The vision of the state government : “The Government of Rajasthan would leverage Information & Communication Technology (ICT) not only as a tool for improving governance and employment opportunities, but also more significantly as a means to enhance the quality of life & bridging the socio-economic divide in the state.”
Rajasthan is the first state in the country to have a full-fledged Department of Information Technology, established with the advent of IT sector in the country in 1985-86, with more than 3,000 qualified IT professionals working towards realising the e-Governance vision of the state.

In order to provide thrust to e-Governance initiatives across all departments and to make it central to the planning and monitoring process, the state government has taken an enabling stride by allowing all departments to utilise three percent of their respective Plan Budget, for citizen-centric e-Governance initiatives.
It is a first-of-its-kind initiative in the country. Subsequently, it has been made mandatory for departments with citizen interface to roll out at least two citizen services on an end-to-end basis through the CSCs as part of their e-Governance Plan.
The state government’s focus is to use ICT to deliver e-Government that is better equipped to respond to the enhanced aspirations of its people in terms of 24×7 availability of quality government services. The aim is to enable a paradigm shift from the government-centric system to a citizen-centric system of governance, while improving the level of governance within the government departments.
The ICT infrastructure
To transform this vision to reality, the Department of IT&C has put in place the essential ICT infrastructure. We set up a state-of-the-art State Data Centre (SDC) in 2005 from state funds. This data centre acts as the core of the state-level information infrastructure, which in turn integrates geographically distributed data depositories. Subsequently, the National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) funded SDC was also made operational in June 2011 in the new IT building and has been accorded ISO certification.
Similarly, to provide effective administration aimed at facilitating faster decision-making, greater participation and better service delivery to the common man, the Secretariat Local Area Network (SecLAN) was put in place in the year 2005. Currently more than 5,000 nodes are operational within this network. The network has since then been expanded to the Metropolitan Area Network, connecting 43 government buildings to the State Secretariat – the hub of entire administrative activities of the state.
The Rajasthan State Wide Area Network (RSWAN) is in its advanced stages of completion. The network would provide the backbone connectivity to all the vertical and horizontal government locations across the state. With more than 5,000 offices being connected horizontally,the RSWAN is poised to be the largest SWAN in the whole country.
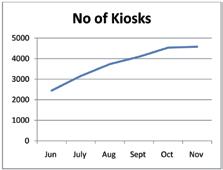
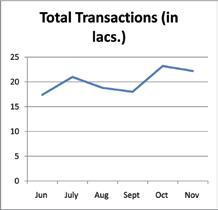
Common Service Centre (CSC) is yet another infrastructure pillar of e-governance that the state government is building in order to ensure “anytime anywhere” web-enabled delivery of government services. The CSC is the the front end for delivering a range of government services and it is worth noting that we are the pioneers of this project.
The Lokmitra Project for urban areas and the Janmitra Project for rural areas – implemented by the state government back in 2002 and then integrated under the brand name of e-Mitra in 2005 – were aimed at creating IT-enabled integrated citizen service delivery system in the form of kiosks. This is where the CSC picked up and was mandated under the NeGP in 2008. As of date, more than 19 lakh transactions are being executed per month through the CSCs in the state.
e-Governance: Citizen at the helm of affairs
Connectivity without content is of no use to anybody. Hence, a number of IT initiatives for citizen-centric service delivery are being implemented and more are in the pipeline.
The first and foremost priority of any government is to ensure citizen satisfaction. We have made an effort in this direction by setting up e-SUGAM – a single window system that ensures delivery of services related to district/ tehsil administration in such a way that the citizens can effortlessly access the services related to caste certificates, domicile certificates, solvency certificate, income certificate, mutation of agricultural land, arms license renewal, etc.
The project acts as a one-stop shop for government services and has broken down barriers by seamlessly linking these services. Up to November 2012, 43,44,590 applications were received in total, out of which 41,27,982 certificates have been issued.
In order to retain the faith of citizens in the Government functioning, our endeavour is to redress any and all government services related grievances of the common man.
For this purpose, we have provided a unique electronic means to the citizens for public grievance registration and redressal through the SUGAM PG Portal – a single-window web-enabled system. Besides the conventional methods of land, e-mail and telephone calls, citizens now have the convenience of registering and monitoring their grievances through the Internet from their homes or from a centre nearest to their homes. Totally 1,36,701 grievances were received through the portal up to November 2012, out of which 99,180 have been disposed off.
Another significant service having a perennial demand, equally in urban and rural areas, relates to the issuance of various certificates for which the citizens had to visit and re-visit the related departments and authorities earlier. In order to eradicate the problem of long queues, time wastage, travel and cost, an online facility of issuing legally-valid and digitally-signed certificates has been launched.
The certificates can be applied for and obtained through Internet from home/single window/kiosk. Currently, the certificates for bonafide resident, caste, income, and solvency are being issued through this facility. The facility is being enhanced to issue other digitally-signed certificates, licenses etc. The popularity and the success of this service can be assessed from the fact that every month approximately 1.5 lakh digitally-signed certificates are being issued.
All of us know that man has always considered agricultural land to be the most valuable asset that any person can possess. In order to facilitate easy and quick transfer of ownership, division and usage of this immovable property – physically and on records – what better way than there be than to digitise the land records of the state?
We were amongst the first states to computerise all land records with major process re-engineering and we have now amended Rajasthan Land Revenue (Land Records) Rules, 1957.
The major achievements of this initiative include replacement of manual handwritten Jamabandi by digitally-signed Jamabandi as the only authentic land ownership record, making Record of Rights (RoR) perennial from quadrennial, thus ensuring regular updated of land records. Major changes in the mutation process have been adopted by making it compulsory to record changes in mutation to online Jamabandi.
Niwai tehsil in Tonk district of the state has been taken up on pilot basis to implement provisioning of digitally-signed Jamabandi to its citizen. The same is to be rolled out in all tehsils in a phased manner.
Moreover, many more citizen-centric and back-office related e-Governance projects are being rolled out by several government departments within Rajasthan. For quick rollout of services and rapid implementation of e-Governance projects, we have laid down guidelines under which generic applications like IT-enabled grievance redressal, e-library, e-office, e-procurement, etc, are being developed by the Department of IT&C, and applications addressing the department-specific needs are being developed by the concerned departments themselves.
In order to facilitate better availability of medical and health services to the citizens, we have implemented Arogya Online – a hospital e-enablement system. Under the project, complete IT-implelmentation of SMS Hospital, Jaipur, has been done. The project is also being implemented in 15 district hospitals, six medical colleges and their associated hospitals.
Another project of the Medical & Health Department is Pregnancy Child Tracking & Health Services Management System (PCTS). Visualising such a system was important which had no precedence anywhere in the country. The project was put to use in 2008 and has resulted in significant improvement in the delivery of health services. Through service messages on mobiles, citizens, health workers and the government departments are able to connect on an one-to-one basis.
As a means to further help the common man, facilitation of online filling of application forms for vacancies published by the Rajasthan Public Service Commission (RPSC) has been provided to the aspiring candidates. This has helped in saving time and cost, avoided postal delays, made admit cards available online, and has also brought about clarity, efficiency and transparency in the working process at RPSC
|
|
| IT infrastructure Services1. No government department / organiations to set up own |
- Data Centre
- Wide Area Network
- CSC like Kiosk
- Call Centre related Software and Services
- SMS Gateway
- Electronic Payment Gateway
2. All departments / organisations to enable their application software to provide services through CSC
Generic Application Software
The following generic applications are available to be used by all departments. They should not develop similar applications at their level.
- e-SUGAM by Administrative Reform for Public Grievance Redressal
- IFMS by Finance Department for Financial Management System
- LITES by Justice Department for Court Cases Monitoring
- Payroll System developed by NIC
- Vidhan Sabha Question Monitoring System developed by NIC
- e-Library deployed by DoIT&C
- e-Office developed by NIC
- e-Procurement developed by NIC
- Biometric Attendance and Leave Management System by DoIT&C/RISL
Hassle-free business with government
While providing convenience to citizens is the primary mandate, we are also facilitating the government- business communication in a major way.
The state governemnt has put in place a mechanism called Single Window Clearance System (SWCS)–an e-Governance initiative for effective, accountable and transparent process of receiving and responding to investment proposals.
It provides a single interface across various departments viz. Bureau of Investment Promotion, Industry, District Industry Centres and other government departments. Further, to strengthen the Single Window System and to give it a statutory status, he state government has introduced a Single Window Act which allows according permissions, invoking and using clearance mechanism within specified time.
For transparency in e-procurement and bidder facilitation, the procurement process within the government departments has been e-enabled and an e-Procurement system has been made mandatory for all departments / autonomous bodies / government undertakings for processing tenders having value of Rs 50 lakh and above through the e-procurement portal of the Rajasthan Government only. In case of PWD, this limit has been reduced to Rs 25 lakh.
Another project called, Rajasthan VAT-IT – an integrated and automated IT system – has been implemented by the Commercial Taxes Department catering to tax payers as well as assesses. The project enables e-registration, e-payment, electronic filing of returns, provision of electronic C-forms besides other routine transactions.
The Rajasthan State Excise Department (RSED) On-line Project facilitates electronic creation, control, monitoring and administration of all types of liquor licenses, permits for all distilleries, breweries, bonds, contractors, wholesalers, shops, hotels, bars, etc, as well as liquor shops in the state of Rajasthan.
Similarly, the aim of making the Department of Mines and Geology (DMG) It-enabled was to improve the system of record keeping, efficient monitoring and control of the various processes and better information dissemination to the stakeholders through an interactive web portal. The stakeholders of the project include miners, lease holders, prospecting minerals exploration companies, various government departments like the Forest Department, Legal Department, Revenue Department & Ancillary Department.
Better governance within government
With a view to improve the quality and level of governance within the government, several initiatives for efficient intra-government communication have also been implemented. The e-Office Application is underway, of which one module – File Tracking & Monitoring System (FTMS) – has already been implemented in a few key departments of the State Secretariat.
The Integrated Financial Management System (IFMS) – an e-Governance initiative of the Government of Rajasthan for effective, accountable and transparent Public Finance Management – has been implemented as an umbrella system covering all modular systems and their integration to ultimately achieve the computerisation of state wide financial transactions and efficient monitoring, including facility for e-payment.
Similarly, an all comprehensive state-wide Human Resource Management System (HRMS) is on the anvil.
Additionally, some departments like Disaster Management & Relief, NREGS, etc, have already implemented their own MIS systems, thus resulting in quick analysis and decision-making.
The State Legislative Assembly is an esteemed institution and the question hour is a vital issue in the proceedings of any State Assembly. Online Answering System (OASYS) – an all-comprehensive online solution, implemented in the state and being used by all the government departments – has helped plug the time delays involved in the delivery and response to questions raised in the Vidhan Sabha. It involves use of digital signatures and SMSes. Again, we are the pioneers to use this system, implemented in 2012, which is now being replicated by other legislative assemblies.
Tapping the potential: Developing expertise in e-Governance
ICT can only be harnessed if appropriate capacity for technology absorption is built. The supply side of e-Governance ecosystem has to become at par with the demand side. In order to ensure this, we have taken steps for adequate capacity building of government personnel across the state. IT literacy has been made mandatory for entry level selection for ministerial posts in the government sector.
Incentives are being provided to government personnel who qualify the IT courses offered by IGNOU and Rajasthan Knowledge Corporation Limited, an organisation set up with the aim of facilitating easy, affordable, recognised IT courses to the masses as well as the government personnel.
Rajasthan is also one of the major beneficiaries of the central government’s e-Governance Champion Programmes for government officers. Nearly ten officers are being nominated every year since the last three years to various programmes sponsored by the Government of India at T A Pai Management Institute, Manipal, and IIM, Indore.
With the collective vision, commitment, technological, managerial and entrepreneurial skills within the government, Rajasthan is well poised to usher in a new era in e-Governance.
Be a part of Elets Collaborative Initiatives. Join Us for Upcoming Events and explore business opportunities. Like us on Facebook , connect with us on LinkedIn and follow us on Twitter, Instagram.











